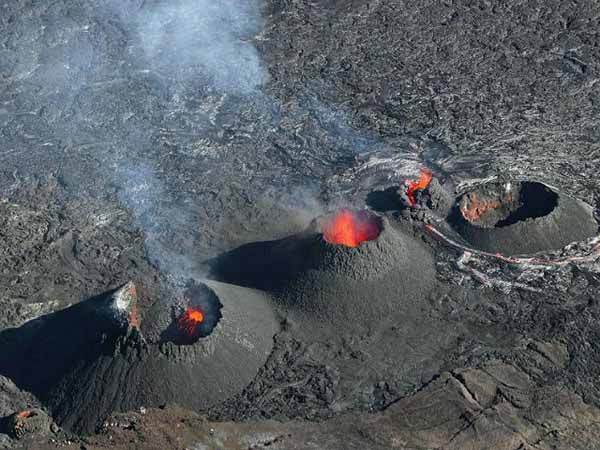
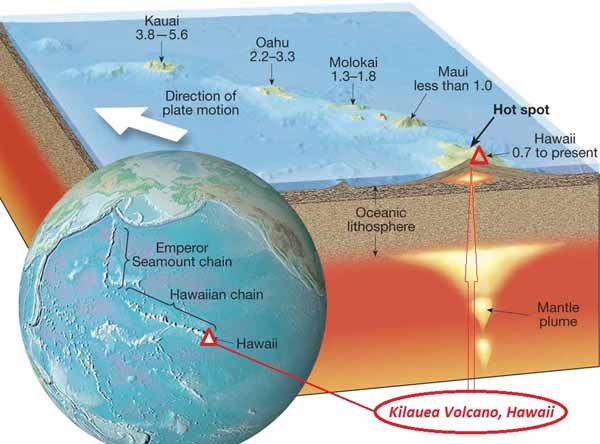
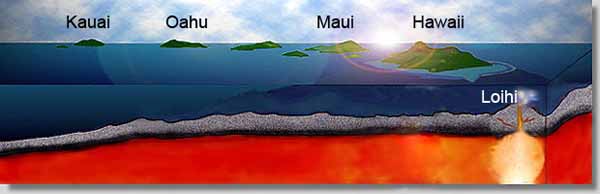
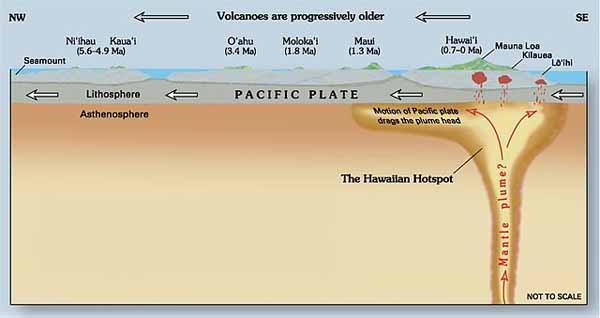
Kilauea is a currently active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands, and the most active of the five Hawaiian volcanoes. Kilauea is the most active volcano on the Earth. Located along the southern shore of the island. Coordinates: 19°25’16″N; 155°17’13″W, Summit Elevation: 1247 m. Kilauea’s current eruption dates back to January 3, 1983, and is by far its longest-lived historical period of activity, as well as one of the longest-lived eruptions in the world; as of January 2011, the eruption has produced 3.5 cubic kilometers of lava and resurfaced 123.2 km2 of land. Volcano Kilauea is between 300,000 and 600,000 years old. Volcano emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. It is the second youngest product of the Hawaiian hotspot and the current eruptive center of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain. Structurally, Kilauea has a large, fairly recently formed caldera at its summit and two active rift zones, one extending 125 km east and the other 35 km west, as an active fault line of unknown depth moving vertically an average of 2 to 20 mm per year.
Hawaii Kilauea Volcano Eruption&Lava Flow. Video.